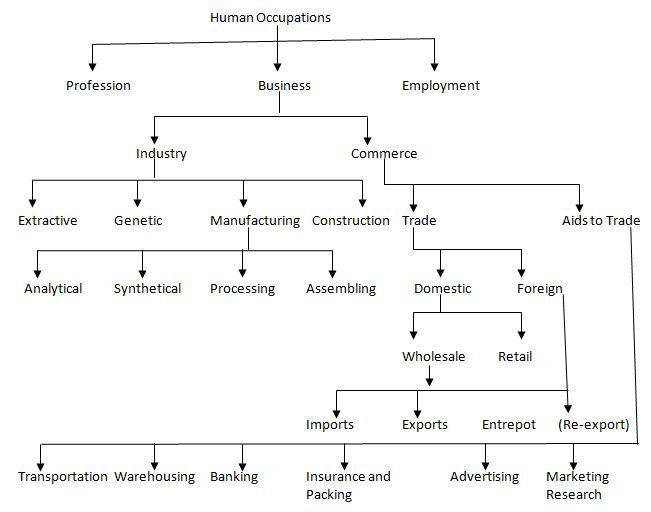
Industry
Industry is that of business which is concerned with the production of goods and services. The term industry is used to refer to the processes by which useful things are extracted from the environment, and transformed, processed, fabricated and multipled into other products. Industry is of the following types:
- Extractive Industries: These industries extract or draw out various products from natural sources such as earth, soil, water, air, etc. The products raised by these industries are provided by nature and collected by human beings. Agriculture, mining, hunting, fishing, lumbering, oil-exploration, quarrying, etc. are examples of extractive industries. The products of such industries are used by manufacturing and construction industries.
- Genetic Industries: Genetic implies heredity or parentage. Genetic industries involve multiplying or reproduction of certain species of plants and animals. Forestry, plant breeding nurseries, cattle breeding farms, poultry farms, fish farms, hatcheries and commercial kernels are examples of genetic industries.
Human Occupations and Branches of Business.
- Manufacturing Industries: These industries are concerned with the conversion or transformation of raw materials and semi-finished products into finished products. Such industries, therefore, create ‘form utility’, manufacturing industries supply most of the products for daily use. Goods supplied by these industries are known as factory production. Manufacturing industries are of the following types :
a) Analytical. In an analytical manufacturing industry. A basic raw material is analysed or separated into a number of products. For instance, an oil refinery separates crude oil into kerosene, gasoline, diesel oil, lubricating oil and petrol.
b) Synthetical. In these industries, two or more materials are combined or mixed together to manufacture a new product. For example, cement is produced by mixing concrete, gypsum and coal.
c) Processing. The industries are engaged in the processing or raw materials through different stages of production. Examples or processing industry include textiles, sugar, steel, etc.
d) Assembling. In this case, various components or parts are brought together to produce a finished product. Manufacture of bicycles, radios, televisions, watches, automobiles are typical examples of assembly industry.
- Construction Industries: These industries are engaged in the erection or construction of buildings, bridges, dams, canals, etc, marble, bricks, etc, and also the products of extractive industries, e.g., stone, marble, bricks, etc. and also the products of manufacturing industries such as cement, iron and steel, wires, etc. These industries create the basic infrastructure for development by employing the process of fabrication. The distinguishing feature of these industries is that their products are made or fabricated at fixed sites. Their products are not carried to the market for sale.