Expenditure Method of National Income
The income generated by the economy by way of production of goods and services can be disposed of in two different ways. It can be either expenditure on consumer goods or expenditure on investment goods. In expenditure method of measuring national income, we only take into account final expenditure. Intermediate expenditure on goods used for further production should be excluded to avoid the problem of double counting. This method is also called the ‘Income Disposal Method’ or ‘Consumption and Investment Method.’
Definition
Expenditure method refers to that method of measuring national income in which the final expenditure on gross domestic product is estimated at market price in an accounting year.
Steps in Expenditure Method
We should follow following steps while calculating national income by the expenditure method.
Step (I)
Identification of Economic Unit
The first step involved in the process is the identification of economic units incurring final expenditures. All the economic units which final expenditure can be broadly divided into four broad sectors. They are (1) Household sector, (2) Producer sector, (3) Govt. sector and (4) Rest of the world sector.
Step (II)
Classification of final Expenditure
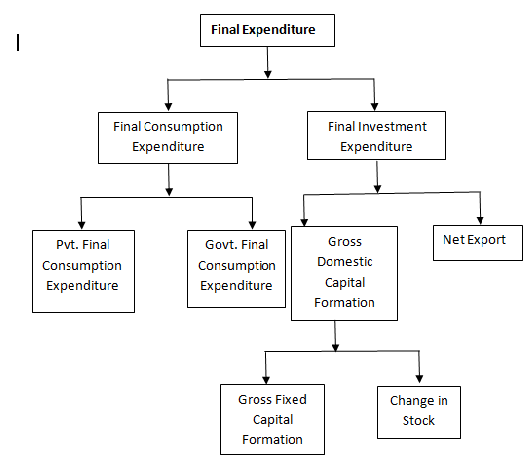
The second step involved in the process is the classification of final expenditure. In final expenditure method, national income is defined as the sum of final expenditure on goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country within one year. This total final expenditure is equal to the GDP at market price.
The final expenditure is classified into the following types
Final consumption Expenditure
(a) Final expenditure on private consumption
(b) Final expenditure on consumption Govt.
Final Investment expenditure
(a) Gross domestic fixed capital formation.
(b) Expenditure on inventories
(c) Net exports
Step III.
Measurement of Final Expenditure
The third and final step involved in the process us the measurement of final expenditure.
For this purpose, we need the following two things:
- Total volume of sales in the market
- Retail prices
With data relating to total volume of sales and retail prices, we can compute the different components of final expenditure as follows:
Final Consumption Expenditure
It is two types
(i) Private final Consumption Expenditure
To calculate the private final consumption, we have to multiply the final sale of consumer goods and services by retail prices. Production for self-consumption has to be added through its imputed values, so also the imputed rent of owners occupied houses.
(ii) Govt. final Consumption Expenditure
This includes expenditure on defence, law and order, education, health, sanitation etc. To measure Govt. final consumption expenditure, goods purchased by the Govt. must be multiplied by the retail prices. Compensation of employees is added, so also the purchases from abroad.
Gross Domestic Capital Formation
Gross domestic capital formation has two components. (i) Gross fixed capital formation, (ii) Changes in stock.
(i) Gross fixed capital formation
It includes the expenditure on construction and expenditure on machinery and equipment. The volume of their final sales is multiplied by the retail prices prevailing in the market. Gross investment includes expenditure on expenditure on depreciation of capital goods. In calculation of NNP, depreciation investment is excluded.
(ii) Expenditure on change in stock
Inventories or change is stock is a component of investment expenditure. The change in stock is calculated by deducting opening stock from closing stock. The balance stock when multiplied by the market price, what we get is the value of inventories.
Net Exports
Net exports refer to the difference between exports and imports of a country during an accounting year. Exports refer to the sale of gods and non-factor services by one country to the rest of the world and imports refer to the purchase of goods and non-factor services from the rest of the world. The difference is the net exports.
Net Exports = Exports – Imports
Net export is a part of domestic product. It may be positive or negative.
It may be noted that if net factor income from the rest of the world is added with net exports, we get net foreign investment. If net foreign investment is taken into account, we would get national product rather than domestic product.
Gross domestic product at market price = Private final consumption expenditure + Govt. Final consumption expenditure + Gross domestic capital formation + Net exports
By adding net factor income from abroad in the GDP at market price, we get gross national product at market price.
By deducting depreciation from GNP at market price, we can get NNP at market price.
Precautions
- Expenditure on second hand goods should not be included.
- Expenditure on shares and bonds should not be included.
- All Govt. expenditures on transfer payments are to be excluded as they do not reflect any production of goods and services.
- All expenditure on intermediate goods and services should be excluded to avoid the problem of double counting.
- Gross investment expenditure is included in total expenditure. Hence to get the national income, we have to deduct the depreciation.