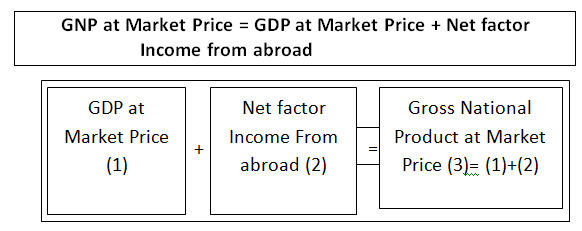
GNP at Market Price
Gross National Product (GNP) is a broader concept. It is not confined to the domestic territory of a country. National product includes the net income of labour and property employed in the rest of the world in addition to all the constituents of gross domestic product.
Definition
According to Hanson, “The gross national product at market price is defined as the market value of final goods and services produced in the domestic territory of a country by normal residents during an accounting year including net factor income from abroad.”
First of all, we have to multiply the total quantity of final goods and services produced within the domestic territory with the market price.
GDPMP = P × Q
Where GDPMP = Gross domestic product at market price
Q = Total quantity of final goods & services
P = Market price of final goods & services
With gross domestic product at market price, we have to add net factor income from abroad to get gross national product at market price. Net factor income from abroad is the difference between the factor income earned from abroad by the normal residents of a country and income paid for the factor services rendered by non-residents within the domestic territory of the country.
Features of GNPMP
(a) The GNP at market price is not confined to the domestic territory of a country. It includes the final goods and services produced in any part of the world where normal residents of the concerned country work.
(b) The GNP at market price is the GDP at market price plus net factor income from abroad.
(c) The GNP generally includes those goods and services coming to the market for transaction purposes.
(d) Imputed value of some goods and services which do not come to market for sale like owner occupied dwellings, free accommodation to the workers etc. is included in GNP.
(e) The price of goods and services refers to the prevailing market price in the accounting year.
(f) Transfer payments, capitals gains and income earned through illegal means are not included in GNP.
(g) The value of second hand goods, financial capital like shares and bonds are not included.
(h) It includes depreciation allowances.
It is important to note that when net factor income from abroad is positive, GNP will be greater than GDP. When it is negative GNP will be smaller than GDP. If the net factor income from abroad is zero then GNP will be equal to GDP.