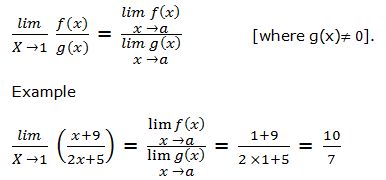Algebra of Limits
1. Additive Method
Under this method, the limit of the sum of any two, or more function say f(X) and g(x) is determined by the following model.
Lim [f(x) ± g(x)] = lim f(x) ± lim g(x)
x→ a x → a x → a
Example
Limit ( x² + 2x + 5 ) = lim x² + lim 2x + lim 5
x→ 0 x→ 0 x→ 0
= 02 + 2 × 0 + 5 = 5
2. Multiplicative Method
Under this method, the limit of the product of any two, or more functions say f(x) and f(g) is computed by the following model:
Lim [f(x) . g(x)] = lim f(x) . lim g(x)
x→ a x → a x → a
Example
Lim (x-4) (x + 5) = lim (x – 4) × lim (x + 5)
x→ 3 x→ 3
= (3 – 4) × (3 + 5) = -8
3. Constantive Method
Under this method, the limit of the product of a constant say K, and a function say f(x) is determined by the following model:
Lim K. f(x) = K lim f(x)
x→ a x → a
Example
Lim 5 x 3 + 3 x 2 – 2x = lim 5 x 3 + lim 3 x 2 – lim 2x
x→ 2 x → 2 x → a
= 5 × 23 + 3 × 22 – 2 × 2 = 48
4. Dividing Method
Under this method, the limit of the quotient of any two functions say f(x), and g(x) is determined by the following model: