Factors of Production
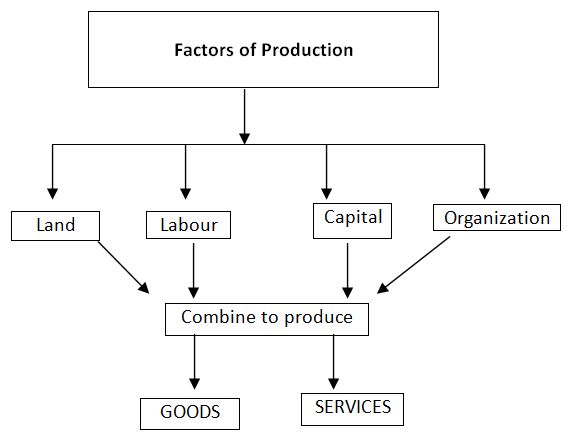
As discussed above production is the creation of utility. But how utility is created or added in the good? In other words how a carpenter makes a chair out of a log of wood? The carpenter need a space to work, some instruments with which he will work and contributes his own labour time for the purpose. In economics these things are known as the factors of production. Therefore anything that helps in the production of goods and services is called a factor of production. In the above example the space or the house needed for the carpenter to work is called land. His own personal efforts are called labour and his instruments are called capital. The classical economists had divided the factors of production into the above three categories. Later the noted neoclassical economist Alfred Marshall introduced organization as the fourth factor of production. Therefore in the traditional classification of factors of production, we have four factors of production like land, labour, capital and organization. Land and labour are called ‘primary’ or ‘original’ factors of production as they constitute the basis of economic activity. Capital, which consists of instruments of production is the product of land and labour. Organisation is only a special form of labour. Below we have discussed these factors of production briefly.
Land
In ordinary language, land refers to the surface of the earth. But in economics land refers to the “productive” resources given by nature and existing in their natural state over the supply of which man has very little control.” Defined in this sense, land includes the earth’s soil with its fertility, climatic conditions, topography, rivers, mountains, forests, mineral deposits etc. That means all natural resources on, over and below the surface of the earth are included in the definition of land. But modern writers have restricted the meaning of land to those natural resources which can be owned by human beings and which can yield and income.
Labour
Any physical or mental effort undertaken with a view to getting a reward in cash or kind is called labour in economics. Any work done for pleasure or leisure is not labour. The work of a mother in rearing up children, the exertion of a football player in the college team are not labour in economics. This is because they do not get any monetary reward.
Capital
Capital is a produced means of production. It is ‘produced’ because it is the product of human labour. It is a means of production because it helps in further production of wealth. Plants, buildings, machines, highways, ports, raw materials etc. are the examples of capital. Thus all economic goods which help in further production of goods and services and thereby satisfy human wants indirectly are called capital.
Organization
Organization is a special kind of labour, it includes the art of Organising business, taking responsibility of decisions and the risks arising there from.The man who organizes business is called the organizer or the entrepreneur.