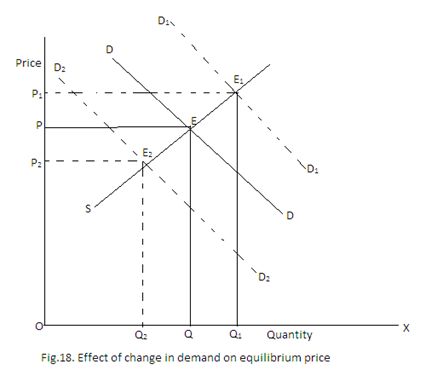
Impact of Change in Demand on Equilibrium Price
Both the forces of demand and supply determine the equilibrium price. Out of the two determinants, if any one undergoes a change, equilibrium price will also change. Here we will discuss the impact of change in demand on equilibrium price.
Change in demand occurs when non-price determinants like income, taste, price of related items etc. undergo a change. If due to the change in any one of the variables, demand changes favourably, demand curve will shift to the right. If there is decrease in demand, demand curve will shift to the left.
In the above diagram, supply remaining constant, there is a change in demand. For example if there is increase in income, then demand curve will shift to the right as indicated by the D1D1 curve. It intersects the original supply curve at E1. As a result, the new equilibrium price is OP1 and the new equilibrium quantity is OQ1. If there is a decrease in income, then demand curve will shift to the left and equilibrium price will fall to OP2 and equilibrium quantity will fall to OQ2.
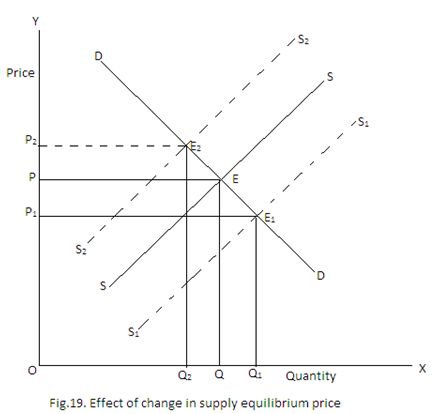
Change in Supply and Equilibrium Price
Demand remaining constant, if there is a change in supply, then also equilibrium price will change. Change in supply occurs when non-price determinants of supply like price of factors, price of related goods, production technique etc. change. As a result supply curve shifts to the right or left.
In the above diagram, DD and SS are the original demand and supply curves respectively. OP is the original price and OQ is the original quantity. Now if there is increase in supply, supply curve will shift to the right as indicated by S1S1 curve which intersects DD curve at E1 to determine OP1 the new equilibrium price. Similarly if there is decrease in supply, the supply curve will shift to the left as indicated by S2S2 curve. The new equilibrium price is OP2 and equilibrium quantity is OQ2.