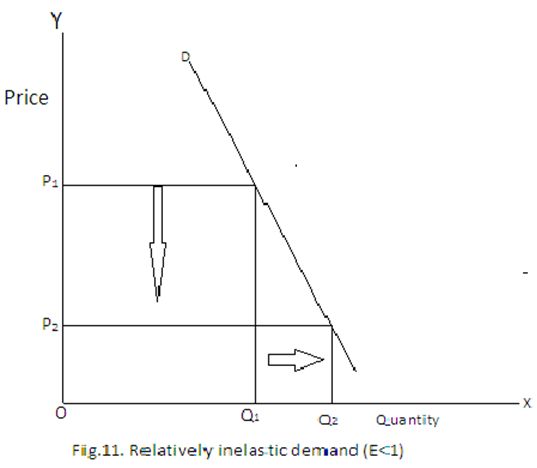
Relatively Inelastic Demand
Demand is said to relatively inelastic when a given change in price produces a less than proportionate change in quantity demanded. For example when a 50% fall in price of a good produces 10% rise in quantity demanded. The price elasticity of demand becomes less than 1. This is illustrated in the following diagram.
In Fig. 11, the demand curve is relatively steep. Here fall in price is P1P2 and rise in quantity demanded is Q1Q1<P1P2 price elasticity is less than one.