Methods of Measuring the Irregular Variations
The irregular variations are very much erratic in nature. They remain so mixed up with the cyclical variations that are very difficult to separate them from the cyclical variation in a meaningful manner.
However, the following methods may be suggested for identifying and isolating them in a time series, some how or other.
1. Additive Model:
Under this model, the irregular variations are identified by subtracting the sum of the other three components of a time series viz : trend, seasonal and cyclical, from its observed value. Symbolically this given by:
I = Y – (T + S + C)
Where I = irregular variation:
Y = observed value i.e. Yc
T = trend value ,i.e. Yc
S = Seasonal value and
C = Cyclical variation.
2. Multiplicative Method.
Under this model, the irregular variations are measured by dividing the observed values in a time series by the product of its other three components viz : T, S and C. Symbolically, this is given by
Under this method, the irregular variations can, also, be identified in any of the following two forms:
- As ratio of the index of cycle & irregular to the index of the cyclical variation and multiplied by 100 i.e. I =
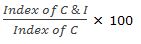
- As a measure of cyclical normalcy (percentage deviation) by deducting 100 from the index of irregular variation.
Thus, Cyclical normalcy or
Percentage deviation = 1 – 100
