Types of Questions in Data Collection
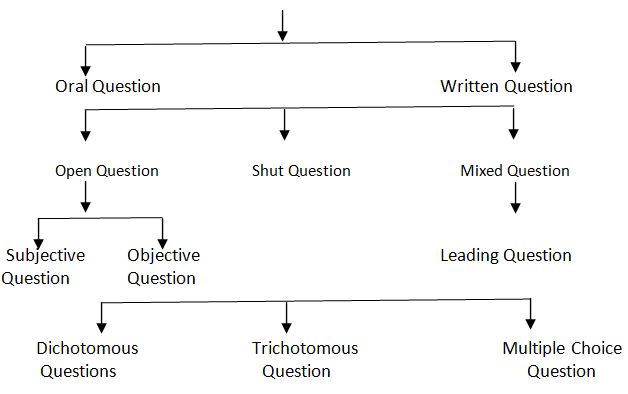
There are several types of questions which can be classified through a chart as under:
Question Chart
Each of the above types of questions is explained here as under:
Oral Question
A question that is put through the words of mouth is called oral question. Such type of questions can be put only when the informant is present on the spot. This type of questions are usually put in the interviews and discussions conducted for some purpose. These questions are likely to be unsystematic, irritative and capricious at times. They should be avoided in the collection of statistical data unless they are backed by some questionnaire or schedule (a list of written questions) set in advance.
Written Question
A question that is put through the words written on a sheet of paper is called a written question. A list of such questions is called a questionnaire, or a schedule. Such type of questions are put to extract, or collect the desired information in a systematic manner from the informants who may or may not be present on the spot of the enquiry. This type of questions can be used for collection of the primary data under any of the methods in common use. These questions can be put systematically, without leaving any room for irritation on the part of the informants, or manipulation on the part of the enumerators. However, these questions can be twisted by an unscrupulous investigator to elicit a wrong reply.
A written question can again be of three types viz. (1) Open question (2) Shut question and (3) Mixed question.
Open Question
An open questions is one in which the respondent is given the liberty to answer to the question in any manner he likes. For instance, “What are the limitations of statistics?” “What suggestions do you like to give for the improvement of the students’ problem?” Which programme in the T.V. do you like most?” are examples of open questions. These questions can be either of subjective, or of objective nature.
Subjective Question
A subjective question is a type of open question which needs the answer in a descriptive manner. For example, “What are the drawbacks of our valuation system? “What are the distrusts of statistics?” are subjective questions the answers to which can be given in a free style only in a descriptive manner.
Objective Question
An objective question is a type of open question which elicits answers in an objective, concrete or definite manner. For instance, “which cinema stars you like most?” “which books on statistics is followed by most of the students of your college?” are objective type of questions that invoke some definite answers.
Shut Questions
A shut questions is one in which the liberty of the respondent in replying to the problem is shut or restricted. In such questions, the respondent is given a number of alternative answers from which he is asked to choose any one as the answer to the question. A shut question can again be of three types viz. (1) Dichotomous question, (2) Trichotomous question and (3) Multiple choice question.
Dichotomous question
A dichotomous question is one in which the possible answers to the question and there is no room for any other answer. For example, “Do you know scootering?” Yes/No, “Do you possess a television set at your home?” Yes/No, are the case of dichotomous questions.
Trichotomous Questions
A trichotomous question is one in which the respondent is given three alternative answers out of which, he is asked to point out any one he feels correct. In such cases three possible answers viz. Yes/No/don’t know, or good/better/best, or bad/worse/worst are added to the question out of which, one is to be chosen by the respondent. Such type of questions are usually put in the reasoning tests and various service selection examinations.
Multiple Choice Question
A multiple choice question is one in which more than three possible alternative answers are given out of which, the respondent is required to tick any one as the answer he deems fit. The answer to such questions may be given in different forms viz. Yes, No, Don’t know, No opinion, occasionally, casually, seldom, etc. each of which is placed against the question for selection, by the respondent. The form of such questions may run as shown in the following examples:
Example 1.
Thick the correct one against the question given below :
Do you use incriminating materials in your examinations:
Yes No Occasionally Seldom
Example 2
Tick the correct alternative given against the questions:
Where from did you purchase the scooter?
NY WA IN CA
Example 3
Point out the correct one from the different alternative given against the question:
How do you go to your college?
on foot on bicycle on rickshaw in bus
Example 4
Tick the correct square out of the alternative given against the question:
What percentage of your total income is spent after your smoking?
Less than 3%, 3% to 5% , 5% to 8% and 8% or more
These questions are very easy to answer on the part of the respondents. They also, save time and facilitate tabulation works. In most of the service selection tests, and entrance examinations such type of questions are advantageously put. However, if the number of possible answers to the question is fairly large such type of questions should be avoided.
Mixed Question
A mixed question is one in which, both the types of open questions and shut questions are clubbed. The following are examples of mixed questions:
Example 5
Where from did you buy the SONY T.V. Set?……and tick the correct square given below:
Its performance is
Extremely good, Satisfactory, Poor, Needs Improvement
Example 6
(i) Which book on statistics do you follow?
(ii) Why do you prefer it?
It is prescribed by the teacher
It contains a large number of questions and illustrations
Its price is comparatively less
Its price is comparatively less
It is readily available in the market
Leading question.
A leading question is one which leads itself to a number of other questions. For example, “Why do you take a particular brand of tea? is a type of leading question. This question leads to several questions subsequently viz.,
(i) Is it less intoxicating
(ii) Is it comparatively cheap?
(iii) Is it readily available?
(iv) Is it preferred for aristocracy and so on?